If your website’s organic traffic is very slow, it’s time to get to work on a complete technical SEO audit. Think of it as a health check for your site.
You will identify crawl issues, speed problems, mobile glitches, and more. Whether you are new to SEO or an experienced marketer, this guide will help you audit your site effectively.
Let’s dig in and tidy up your digital space.
12 Steps to Perform a Full Technical SEO Audit
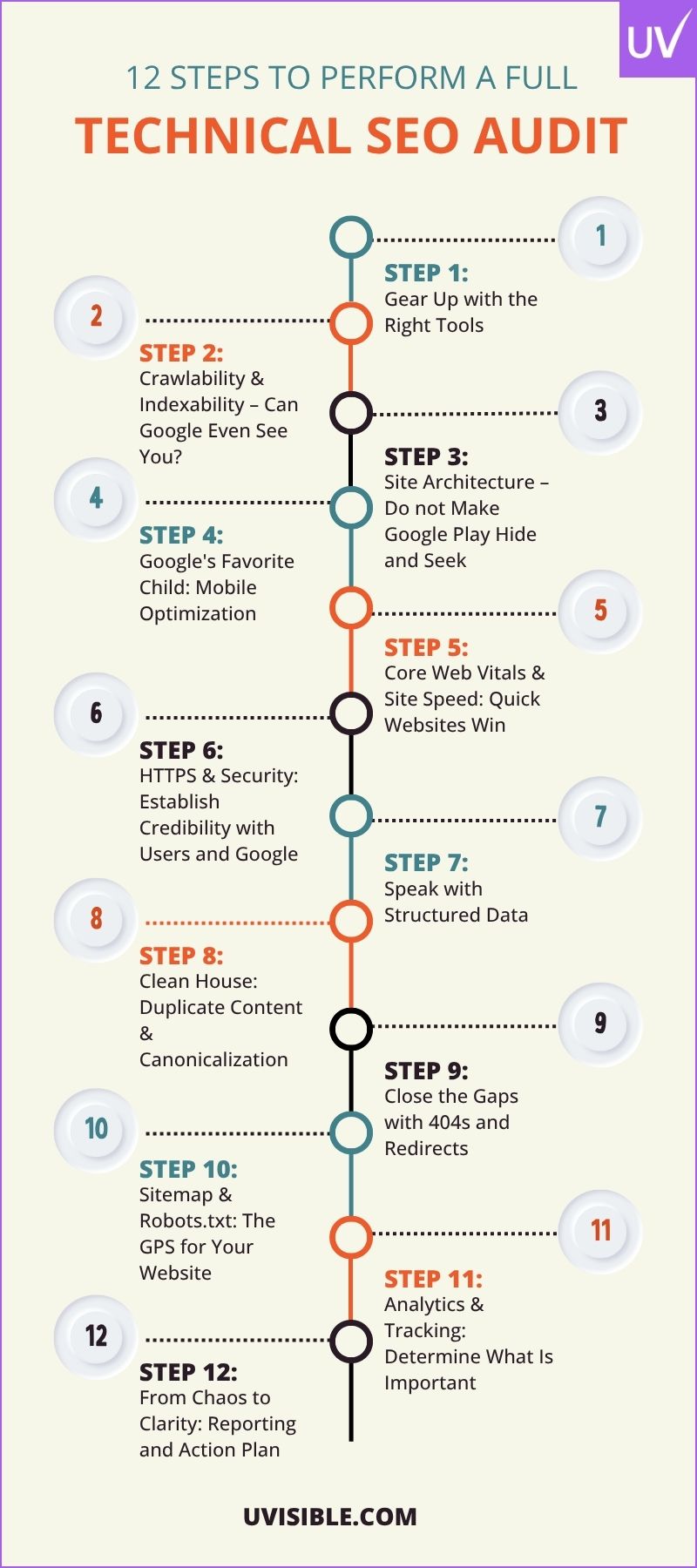
Step 1: Gear Up with the Right Tools
Before you start exploring your site’s backend, you need the right tools. Here are the top ones that will help you audit effectively:
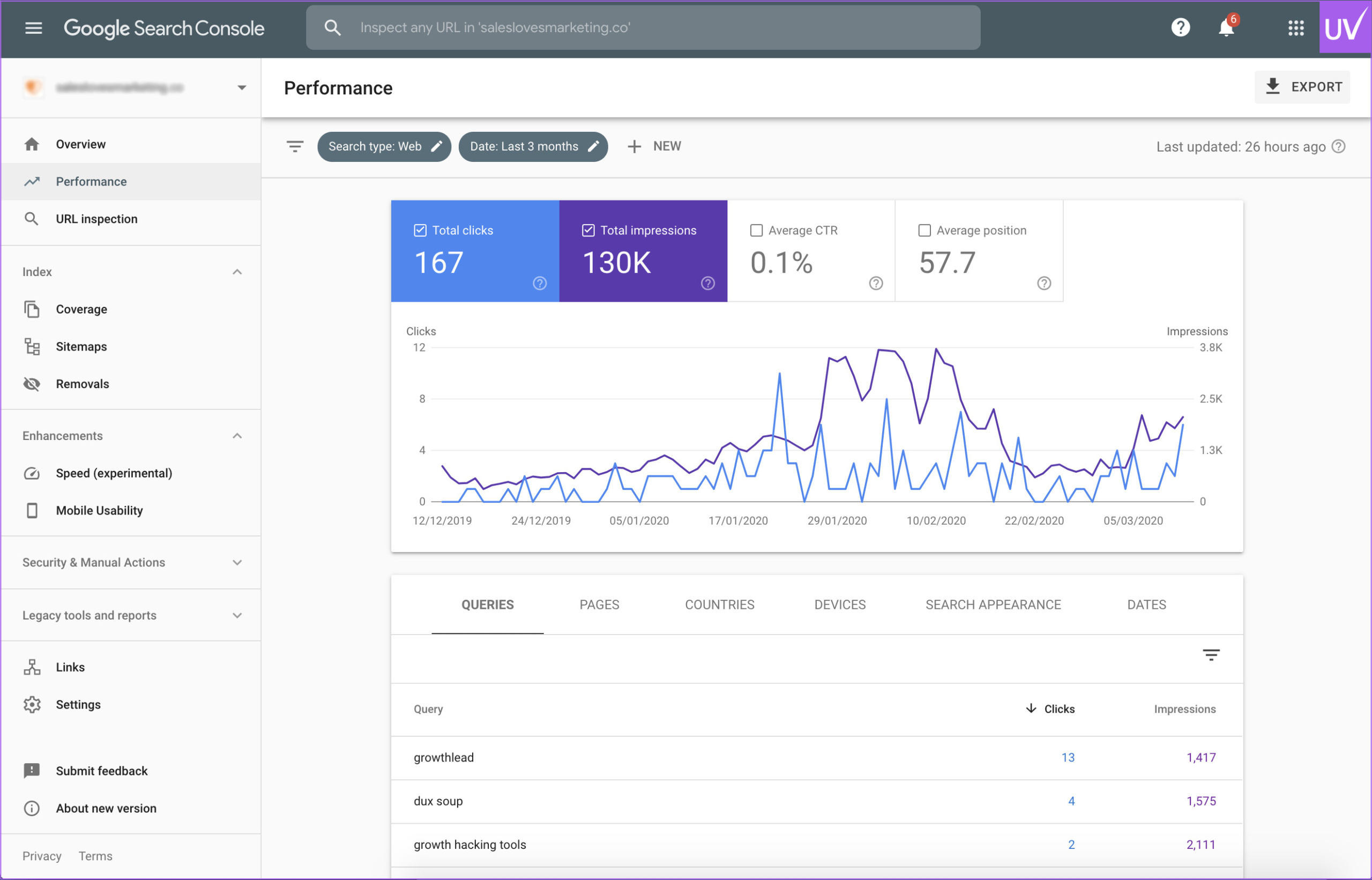
- Google Search Console is your direct connection to Google. It shows crawl errors, indexing problems, and performance metrics.
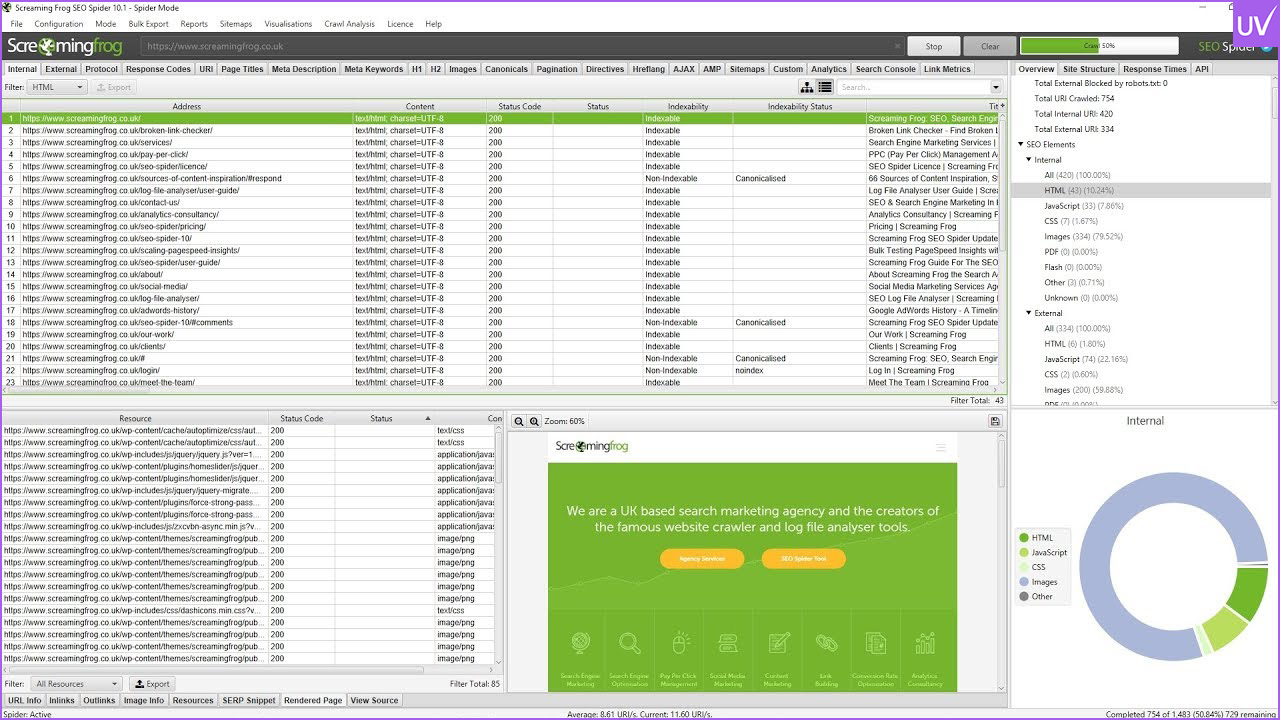
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider is a desktop crawler that behaves like Googlebot. It’s great for finding broken links, duplicate content, and redirect chains.
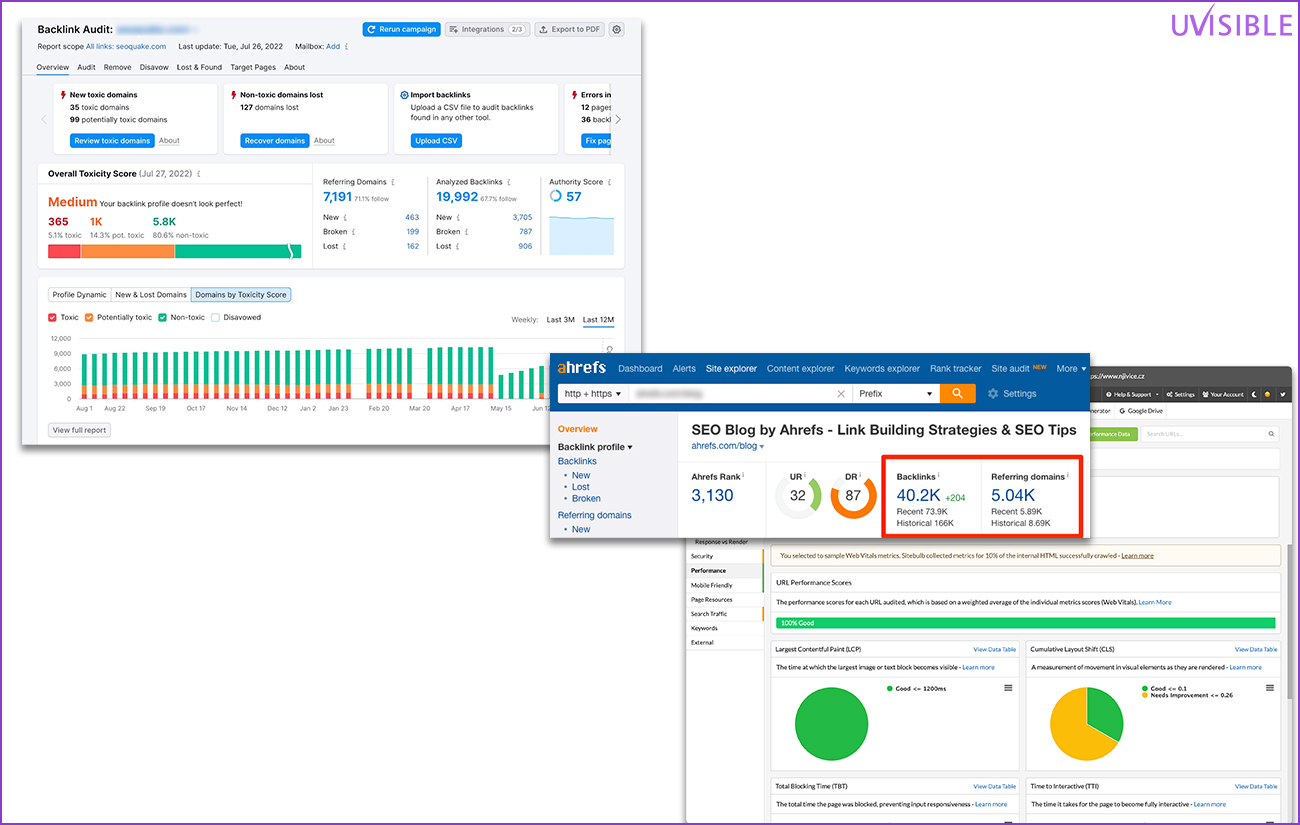
- Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Sitebulb are your go-to tools for backlink audits, keyword analysis, and site health scores.
- GTmetrix and PageSpeed Insights focus on speed. These tools help you check load times and Core Web Vitals.
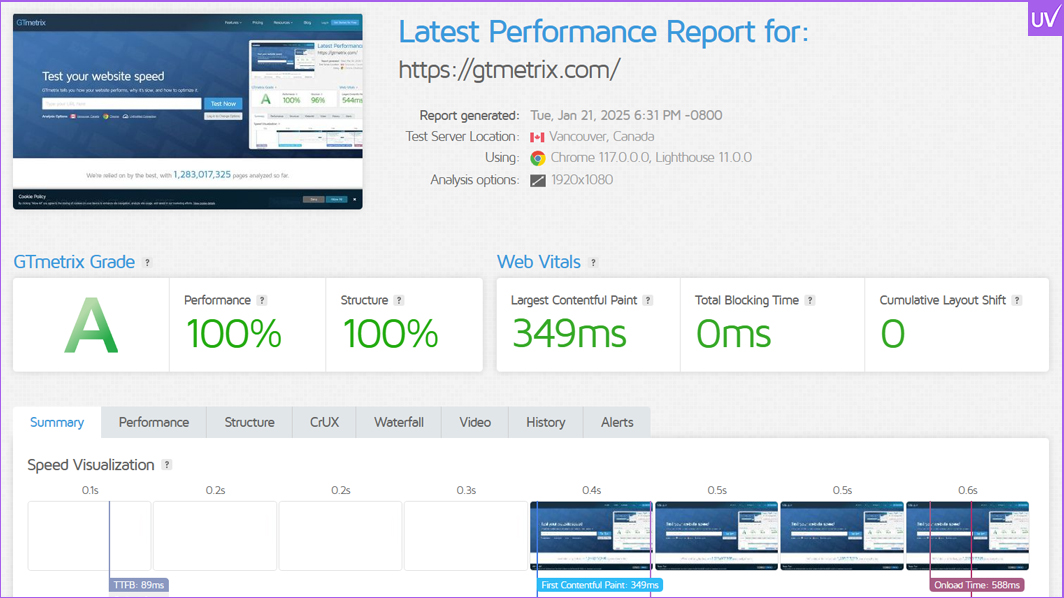
- Web.dev and Lighthouse are useful for thorough performance audits, accessibility checks, and following SEO best practices.
Pro Tip: Use Screaming Frog in conjunction with your Google Search Console and Google Analytics integrations to gain crawl and traffic insights simultaneously.
Step 2: Crawlability & Indexability – Can Google Even See You?
If Googlebot cannot crawl your site, you are essentially shouting into the void. Here is what to check:
Robots.txt
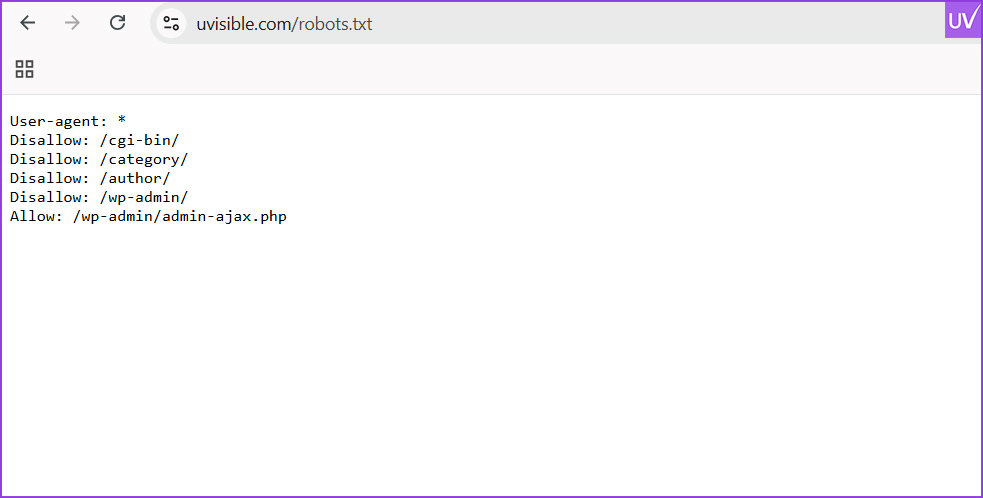
Make sure your robots.txt file does not block important pages. A misplaced “Disallow” can hurt your visibility.
Sitemap.xml
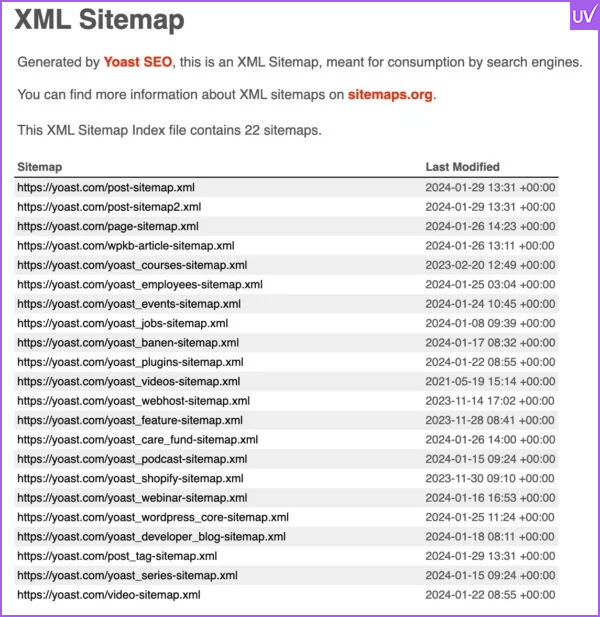
Your sitemap should be clean, updated, and submitted to Google Search Console. It acts as your site’s map for search engines.
Noindex & Canonical Tags
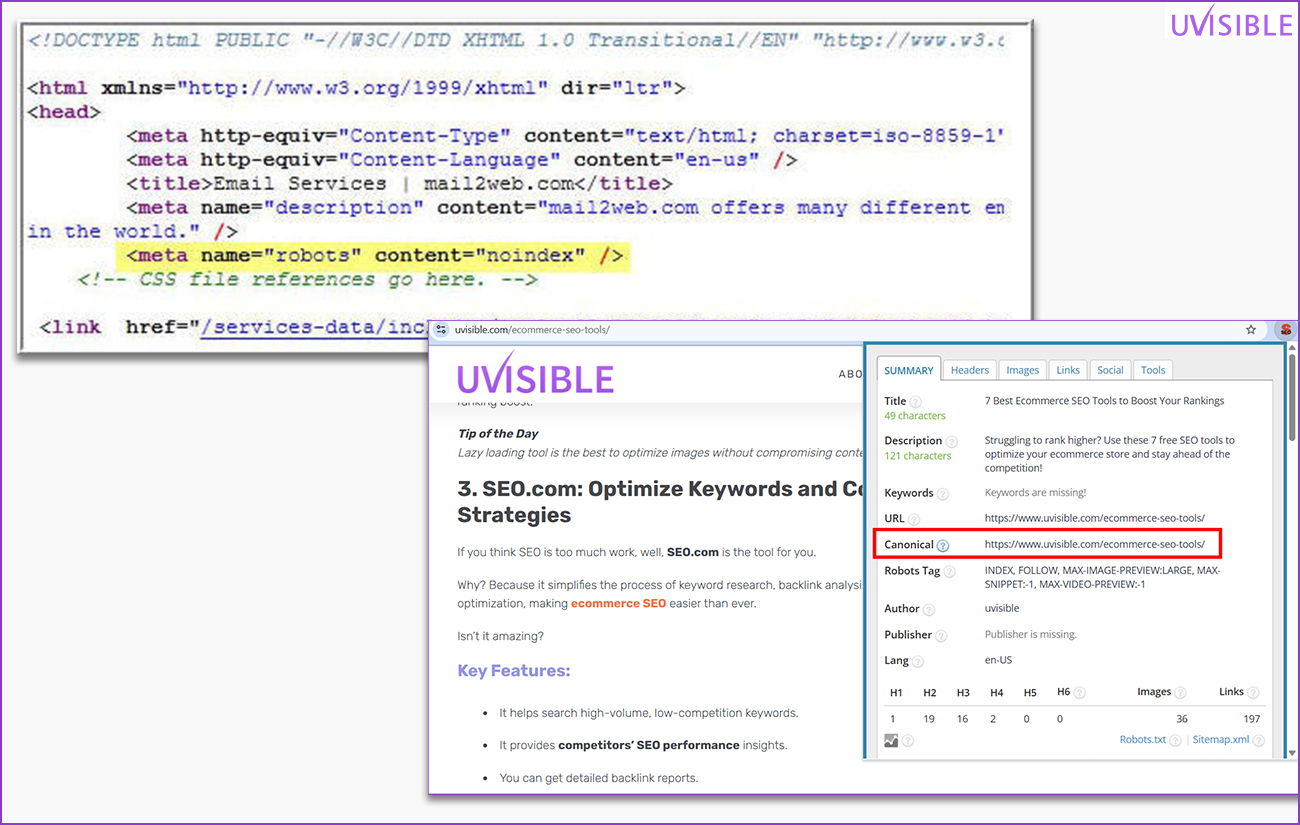
Review your meta directives. Pages labeled “noindex” will not show up in search results. Canonical tags help combine duplicate content.
Crawl Errors
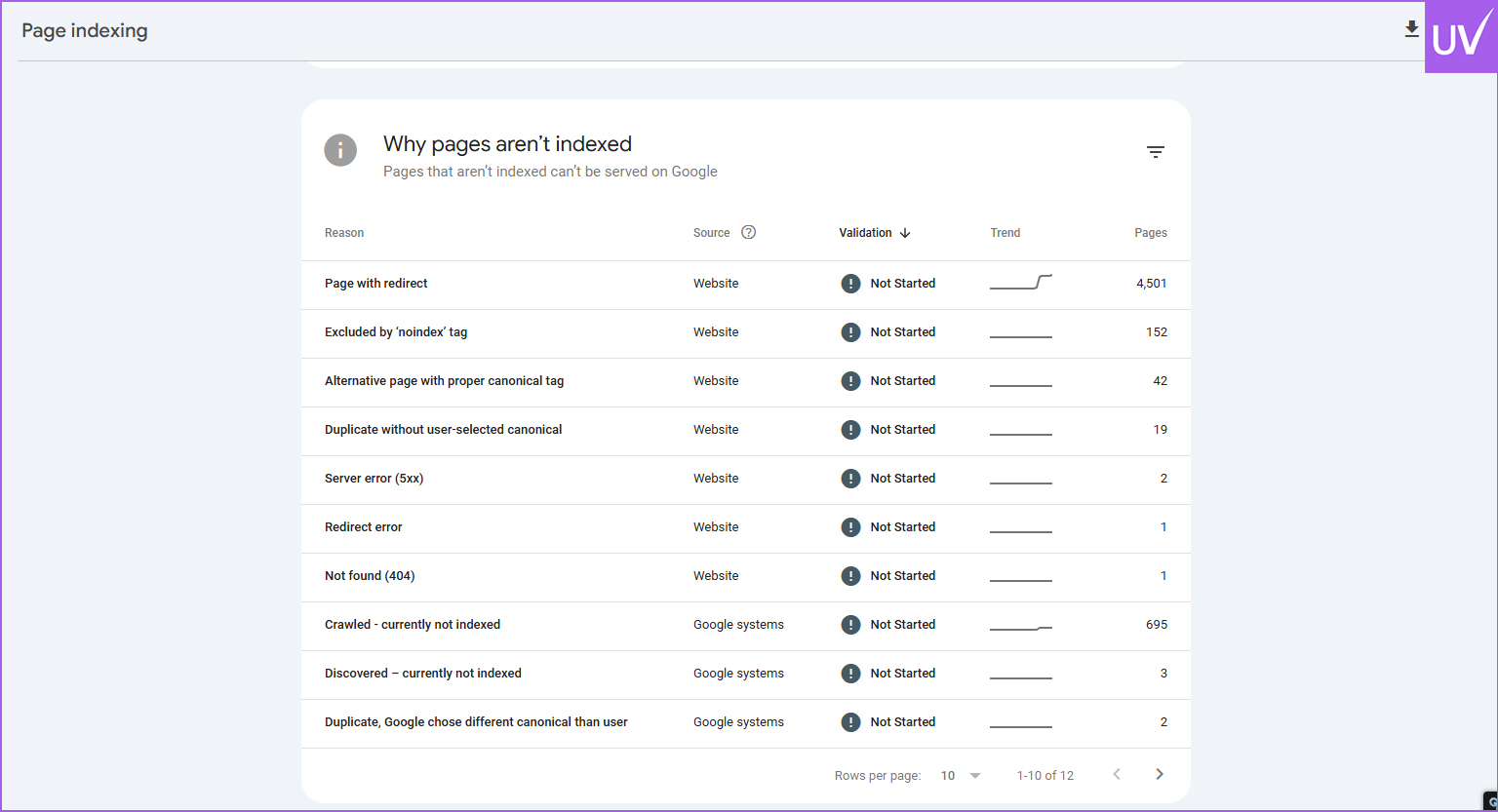
Use GSC and Screaming Frog to find 404 errors, server errors, and blocked resources.
Real-World Example: One client had 70% of their blog posts marked “noindex” because of a faulty plugin. Fixing it led to a 230% increase in traffic within three months.
Step 3: Site Architecture – Do not Make Google Play Hide and Seek
Your site’s structure should be as clear as a well-organized bookshelf.
Flat Architecture
Every page should be reachable within three clicks from the homepage. Deep nesting confuses crawlers and users.
Internal Linking

Link related pages together to improve crawl efficiency and distribute link value.
Orphan Pages
Pages without internal links are SEO dead ends. Use Screaming Frog to find and fix them.
URL Structure
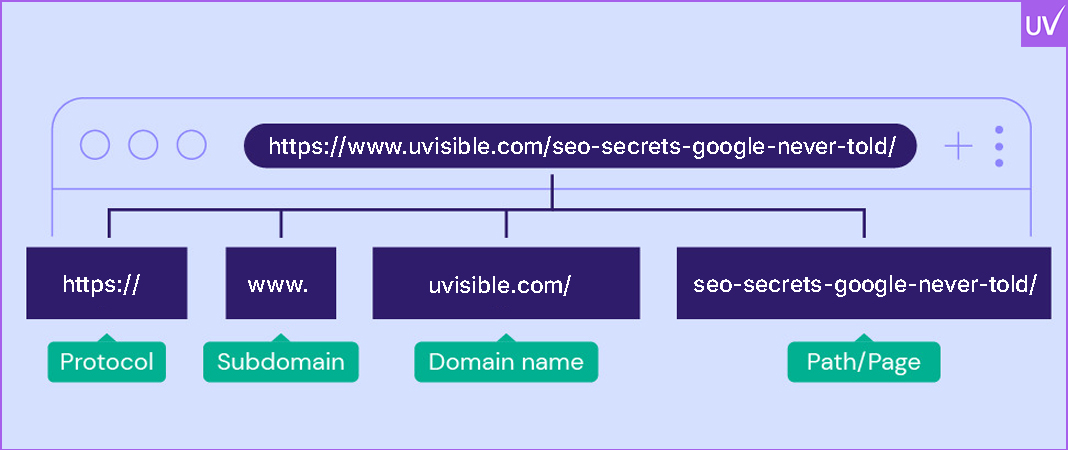
Keep URLs short, rich in keywords, and easy to read. Avoid dynamic parameters like ?id=123.
Stat: Sites with optimized internal linking see up to 40% better crawl efficiency (SEMrush, 2024).
Step 4: Google's Favorite Child: Mobile Optimization
Your mobile user experience is essential since Google shifted to mobile-first indexing.
Mobile-Friendly Evaluation
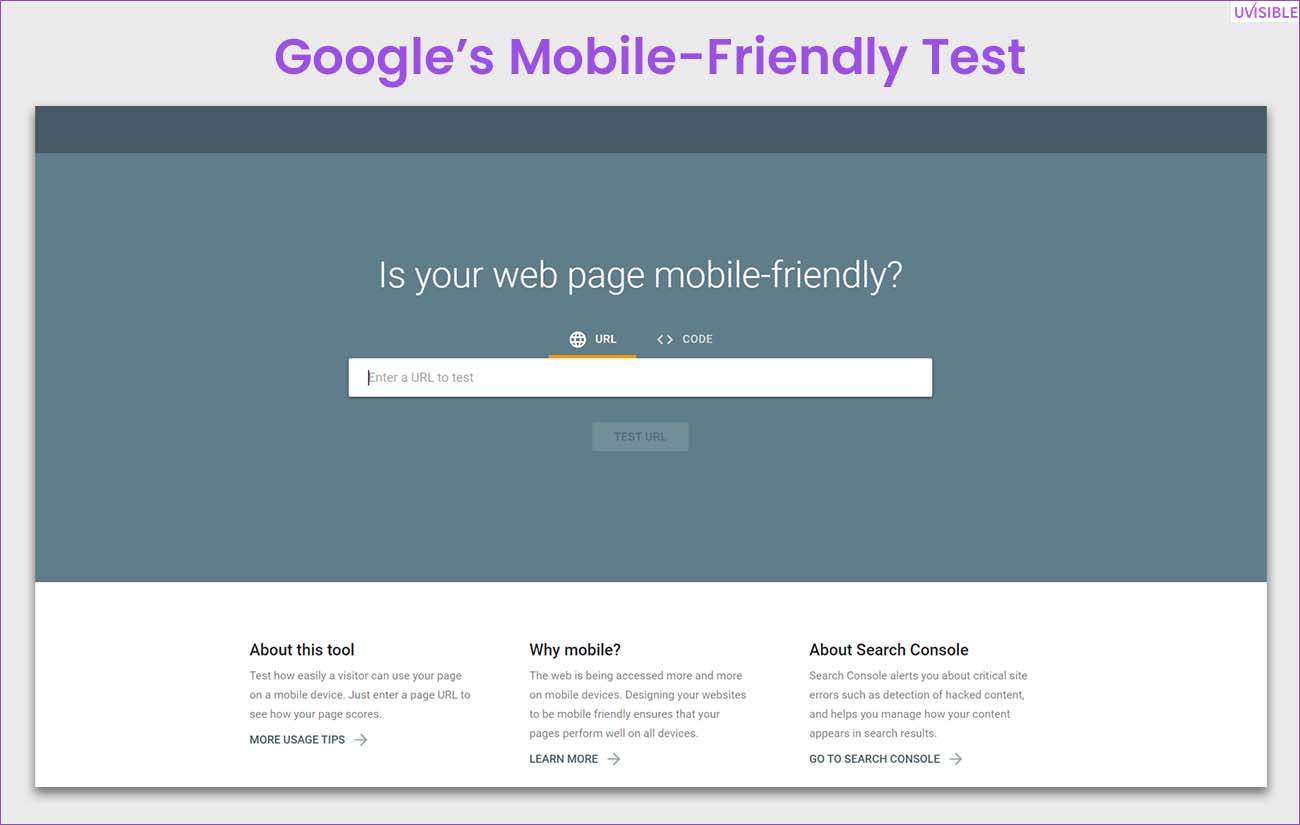
Use Google's Mobile-Friendly Test to assess your website's mobile-friendliness. Resolve any problems with the tap targets, font sizes, and viewport settings.
Design That Responds
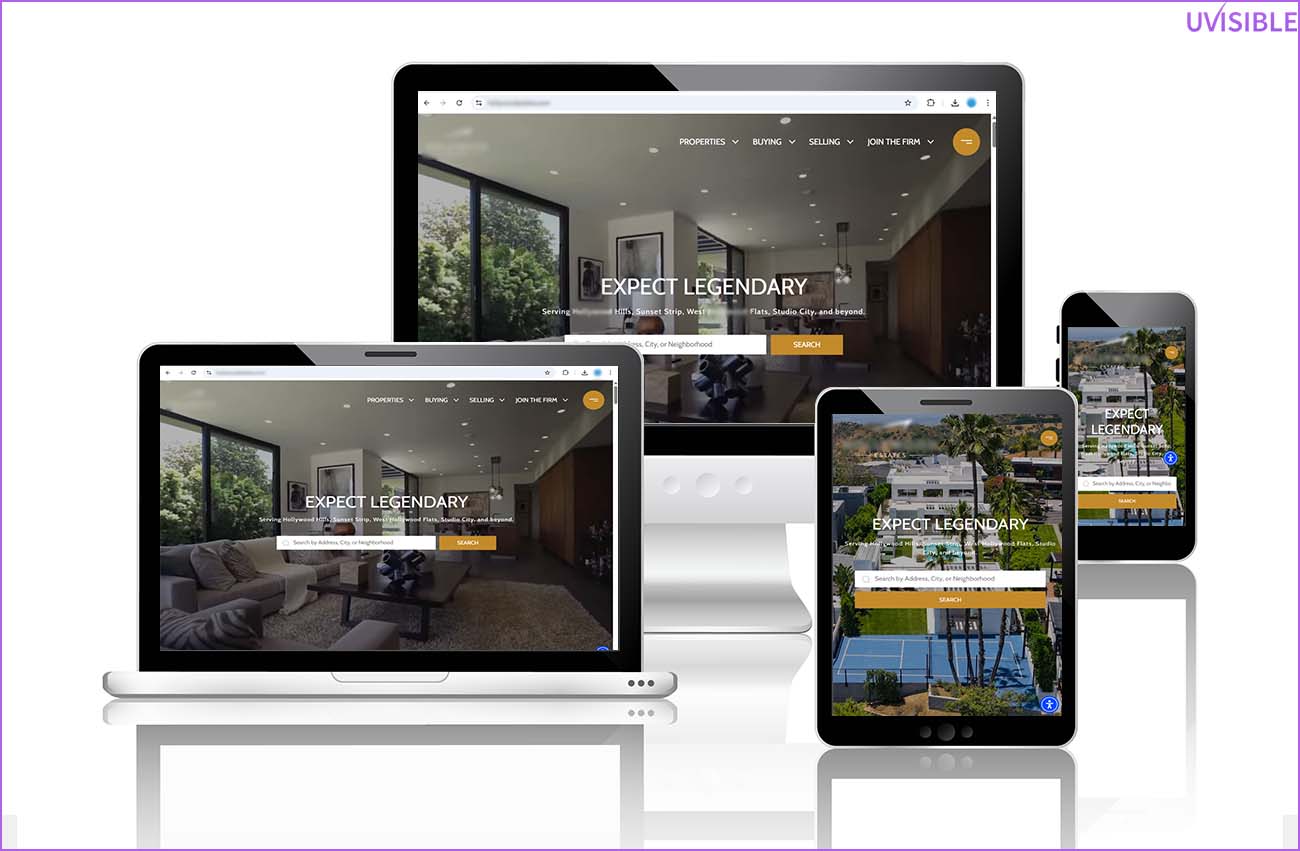
Your website should seamlessly support all screen sizes and resolutions. Steer clear of overlapping elements and horizontal scrolling.
Page Speed on Mobile
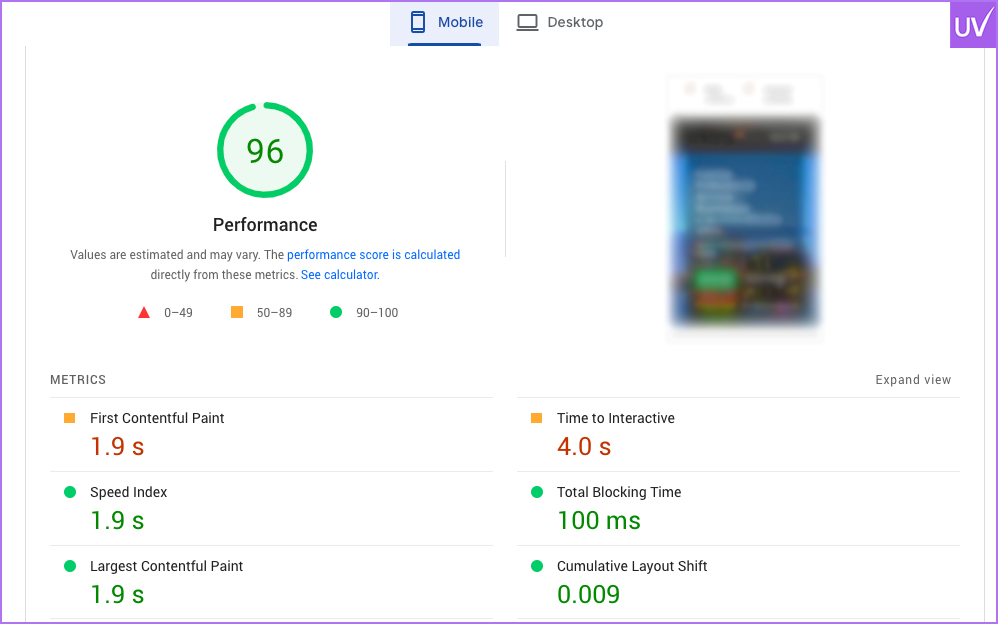
Mobile users are impatient. Use compressed images and lazy loading to speed up load times.
Example: After addressing mobile usability issues, an e-commerce site's bounce rate decreased by 60%.
Step 5: Core Web Vitals & Site Speed: Quick Websites Win
Not only is speed visually appealing, but it is also essential for conversions and rankings.
Core Web Vitals
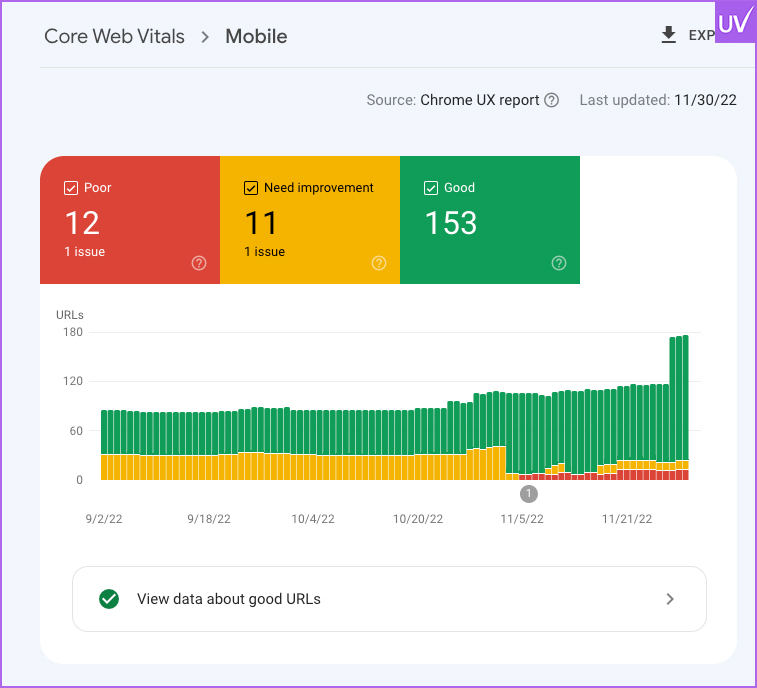
Pay attention to:
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint): It should take less than 2.5 seconds.
- First Input Delay (FID): Less than 100 ms.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): <0.1.
Image Enhancement
Make use of WebP formats, apply lazy loading, and compress images.
Minification of Code
Reduce load times by minifying HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
CDN & Caching
To deliver assets more effectively, use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) and browser caching.
Fact: Conversion rates can drop by 7% with a 1-second page load delay (Akamai, 2023).
Step 6: HTTPS & Security: Establish Credibility with Users and Google
Peace of mind is not the only reason for security. It is a ranking factor as well — something that SEO software and tools often highlight when auditing websites for performance and trust signals.
SSL Certification
Verify that the certificate is valid and that your website is using HTTPS.
Diverse Content
Any HTTP resources on HTTPS pages should be fixed. Browser warnings may result from these.
Headers for Security
Use headers such as X-Content-Type-Options, CSP, and HSTS to defend against different types of attacks.
Example: Within two weeks of moving to HTTPS, a SaaS client experienced a 15% increase in organic traffic.
Step 7: Speak with Structured Data
Google can better comprehend your content and display better results thanks to the Language Schema markup.
Make use of the Rich Results Test
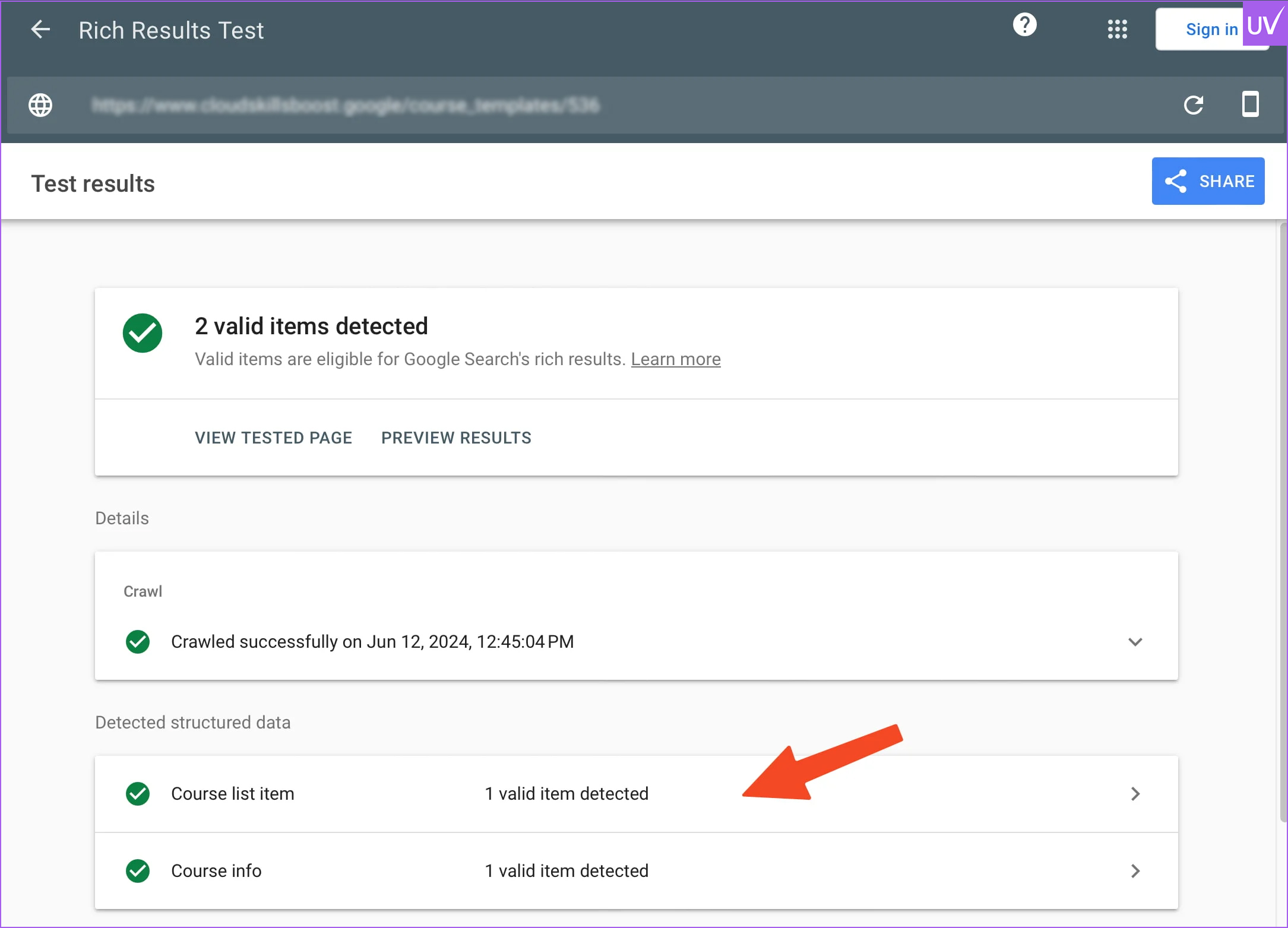
Use Google's tool to validate your structured data.
Use the Appropriate Schema
Include markup for the following:
- Articles
- Products
- FAQs
- Reviews
- Events
Correct Errors
Rich snippets may not show up due to schema errors and warnings.
Stat: Rich snippets are twice as likely to appear on pages with structured data (Moz, 2024).
Step 8: Remove Duplicate Content & Canonicalization
Duplicate content confuses crawlers and reduces your ranking power — a common challenge in content marketing strategies.
Identify Duplicates
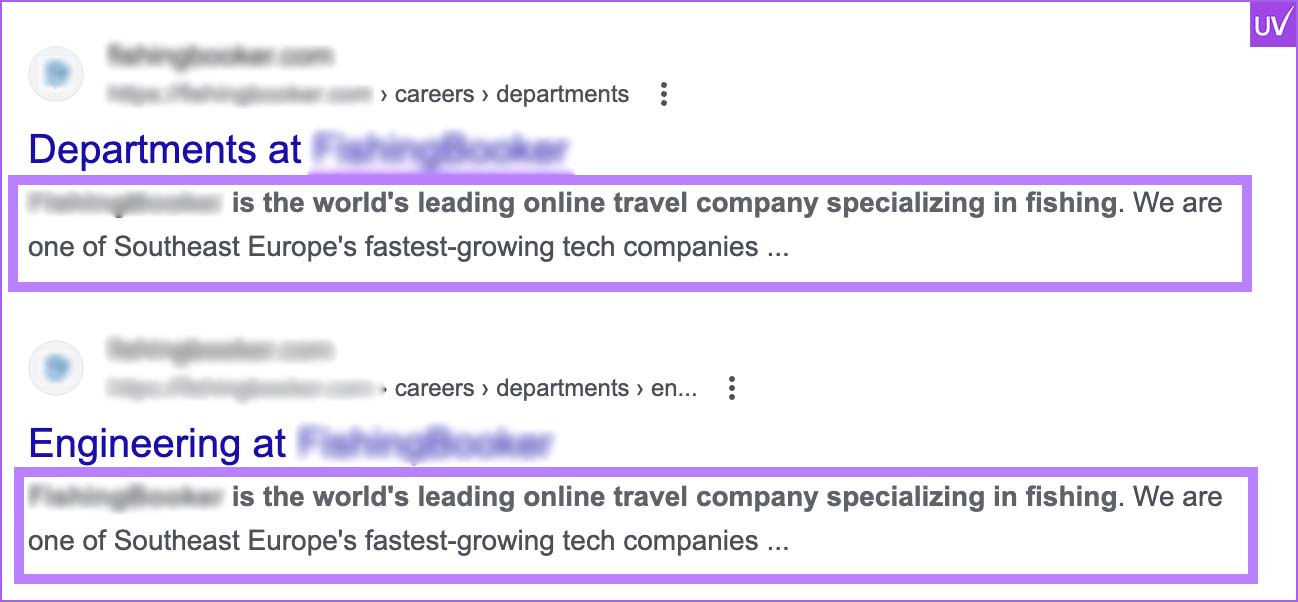
To identify duplicate titles, meta descriptions, and content, use Ahrefs or SEMrush.
Canonical Tags
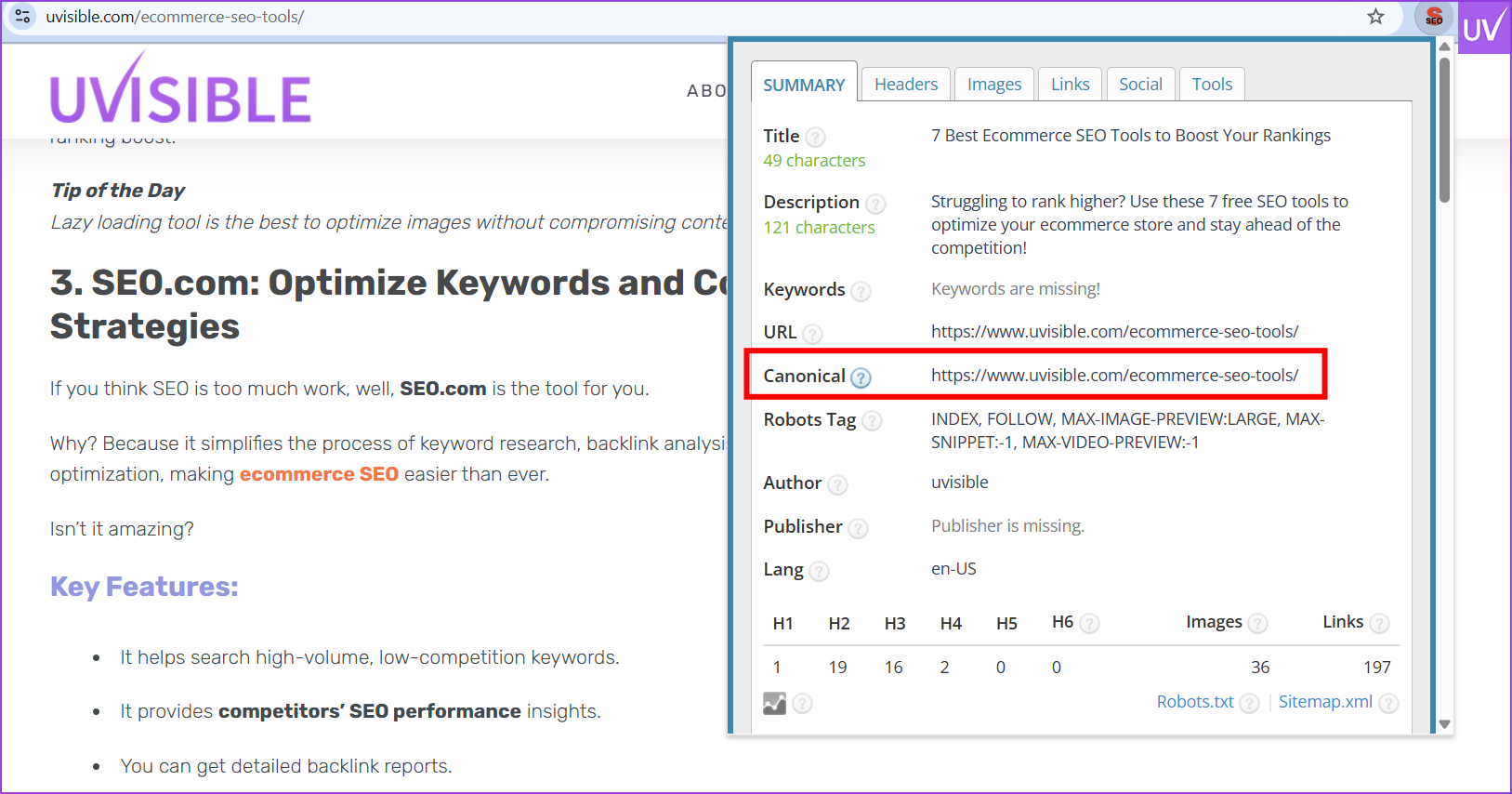
Use canonical tags to direct duplicates to the preferred version.
Minimal Content
Pages that are of little or no use should be removed or combined.
Example: By combining them, a blog with more than 300 similar tag pages saw a 50% increase in crawl budget efficiency.
Step 9: Close the Gaps with 404s and Redirects
Redirect chains and broken links are SEO pitfalls. Using the best SEO extensions can make identifying and fixing them much easier.
Fix 404 errors
Use 301 redirects to reroute broken pages to pertinent content.
Avoid Redirect Chains
Users and crawlers are slowed down by too many hops.
Audits Redirects
All redirects should be mapped out and cleaned up using Screaming Frog.
Fact: According to Web.dev (2023), websites with clear redirect paths typically load 22% faster.
Step 10: Sitemap & Robots.txt: The GPS for Your Website
These files help search engines navigate your website.
XML Sitemap
Make sure it is submitted to GSC, updated, and clean. Add only URLs that can be indexed.
Robots.txt
Important pages shouldn't be blocked. Make good use of "Disallow."
Verify URLs
Make sure sitemap URLs are not blocked and return a 200 status code.
Pro Tip: Audit your sitemap URLs directly by using Screaming Frog's "List Mode."
Step 11: Analytics & Tracking: Determine What Is Important
It cannot be improved if it cannot be measured.
Google Analytics
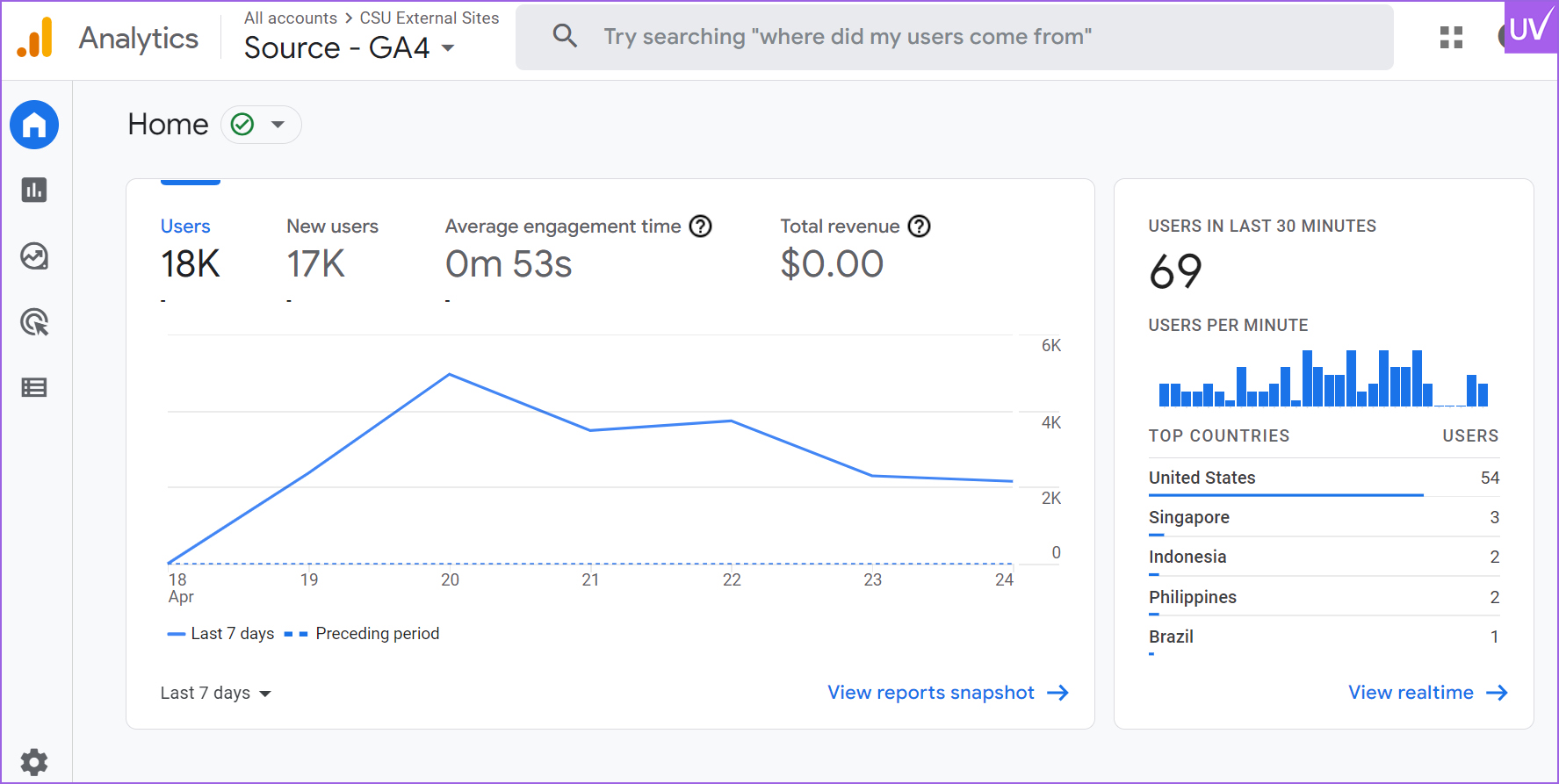
Make sure it is tracking every page and is installed correctly.
Google Tags Manager
For flexible tag deployment and event tracking, use GTM.
Conversion Goals
Establish targets for purchases, form submissions, and other important activities.
For instance, a B2B website discovered duplicate GA tags, resulting in a 30% increase in bounce rate. By fixing it, their actual user behavior became clear.
Step 12: From Chaos to Clarity: Reporting and Action Plan
It's time to take action now that you have discovered every skeleton.
Make an Audit Report
Provide a detailed SEO audit report summarizing the results with key metrics, severity levels, and screenshots. This helps stakeholders clearly understand what needs attention.
Prioritize Fixes
Prioritize high-impact problems first, such as speed, mobile usability, and crawl errors.
Create a Schedule
Assign work, establish due dates, and monitor advancement.
Fact: According to Uvisible client data from 2025, teams that apply audit fixes within 30 days see three times faster ranking improvements.
Final Thoughts: Do not Just Audit—Optimize
A technical SEO audit is a continuous process. It serves as a routine health check for your website. Do it every three months, monitor your progress, and keep up with Google's constantly evolving algorithm.
Keep in mind that SEO is a methodical process rather than a magic trick. Furthermore, technical SEO serves as the cornerstone that keeps everything together.
Don’t want to handle it all yourself? Partner with an experienced SEO outsourcing agency like Uvisible.
For a free technical SEO consultation, get in touch with Uvisible.
We'll audit your website, address any problems, and help you dominate the search engine results page.
About us and this blog
We are a digital marketing company with a focus on helping our customers achieve great results across several key areas.
Request a free quote
We offer professional SEO services that help websites increase their organic search score drastically in order to compete for the highest rankings even when it comes to highly competitive keywords.
Subscribe to our newsletter!
More from our blog
See all postsRecent Posts
- How SEO Works in Bing (And Why Ignoring It Might Be Costing You More Than You Think) February 27, 2026
- Things Every Website Should Have: The Complete SEO Blueprint February 14, 2026
- Digital Marketing Conferences 2026: Top Global Events for Marketing Leaders February 7, 2026







Pingback: AI Didn’t Kill SEO — It Made White Label SEO Essential for Agencies